Describe the Function of Platelets Quizlet
The function of platelets is to repair small blood vessels and prevent dangerous amounts of blood from leaking out. Adhesion to endothelium to initiate homeostasis Activation of intracellular signaling cascade to cause crystal changes and granule release to form plug Support thrombin generation as a surface of coagulation cascade Describe platelet adherence Vessel injury exposes subendothelial components.

31 Histology Platelets Diagram Quizlet
Describe the make-up of human blood and state the roles of plasma plasma proteins where they are made red blood cells platelets and leukocytes.

. What is the function of fibrin. Discuss the reasons why blood should clot. 71 Describe the composition and functions of the blood.
They get their name because they look like a plate. Blood platelets are discoid cellular fragments without nucleus originating from megakaryocytes. Releasing enzymes and other factors at the propriate times.
Explain in detail the carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffering system ie. They are fragments of cytoplasm which are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow and then enter the circulation. D They carry oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Dissolve blood clots when they are no. Platelets then change their shape adhere to newly exposed subendothelial tissues release the. Platelets were once called thrombocytes.
Be able to duplicate the equation and explain in which direction the equation would proceed under certain conditions and. The primary function of platelets is to aid in the blood clotting process. In addition to sealing vascular breaks platelets play an almost continuous role in maintaining normal vascular integrity.
The platelets are made in the bone marrow have a flat disc-shape and are smaller than the white or the red blood cells. What is the function of platelets. Most of your platelets.
Important to the clotting process formation of temporary patch in the walls of damaged bld ves active contraction after clot formation has occurred. Which of the following is a function of platelets. Following their formation from megakaryocytes platelets exist in circulation for 57 days and primarily function as regulators of hemostasis and thrombosis.
Platelets have no nucleus. 11 Define Anatomy and Physiology. When activated these cells adhere to one another to block the flow of blood from damaged blood vessels.
It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen which causes it to polymerize. How long do platelets circulate. A They phagocytize pathogens and foreign debris.
Platelets are anucleate blood cells that circulate in amounts of 150 to 400 10 9 L with mean counts slightly higher in women than in men. Secrete vasoconstrictors which constrict blood vessels causing vascular spasms in broken blood vessels. Platelets also known as thrombocytes are special blood cells.
The polymerized fibrin together with platelets forms a hemostatic plug or clot over a wound site. O Infection o Volume o Oxygen production o Tissue damage o Healing. Hormonal Influences on Early Platelet Development.
Secrete procoagulants clotting factors to promote blood clotting. In other cases you may have too many platelets in your blood. Fibrin also called Factor Ia is a fibrous non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood.
Following vascular insult or injury platelets become activated in the blood resulting in adhesion to the exposed extracellular matrix underlying the endothelium formation of a. When the platelets gather at a cut blood vessel they give off. When a person is cut platelets rush to the area and cling to the blood vessels that have been damaged sealing them.
Some people have a low platelet count which puts them at risk for uncontrolled bleeding. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Hemostasis is designed to maintain the integrity of the vascular compartment.
Platelets play an important role in the vessel. Platelets circulate in blood plasma and are primarily involved in hemostasis stopping the flow of blood during injury by causing the. Other major blood components include plasma white blood cells and red blood cells.
These cells control blood clotting to heal a wound and stop the bleeding. B They transport lipids and some hormones through the circulation. Platelets have a peculiar function of initiating blood clotting.
Platelets also called thrombocytes are the smallest cell type in the blood. Platelets initiate and control the clotting process. Platelets can also be known as thrombocytes which is part of the components of blood.
Form temporary platelet plugs to stop bleeding. 1 Platelets trigger primary hemostasis on exposure to endothelial subendothelial and plasma procoagulants in blood vessel injury. Start studying 72 73Describe the Structure and function of Erythrocytes Leukocytes and platelets Outline the Erythrocyte production.
This process takes place when blood vessels are cut. Platelets Platelets also called thrombocytes are blood cells whose function along with the coagulation factors is to stop bleeding. Platelets are able to respond to a great variety of agonists which bind to specific receptors localized on the plasma membrane.
Abstract The main function of platelets the maintenance of hemostasis depends on three of their properties the endothelial supporting function of platelets the ability to form hemostatic plugs and to release lipoprotein material platelet factor 3. C They reduce blood loss from damaged blood vessels. Platelets have the following functions.
What Are Platelets. Blood clotting is the process by which blood loses its liquid state or. It also forms the element of blood which includes erythrocytes red blood cells leucocyte white blood cells and thrombocytes platelets itself.

Platelets Hemostatic Plug Flashcards Quizlet

Platelet Production Structure And Function Flashcards Quizlet

Platelets In Health And Disease Diagram Quizlet

Bone Marrow Medical Laboratory Science Medical Anatomy Medical Student Study

Dsa 2 Platelet Function Hemostasis Dsa Flashcards Quizlet

Platelets Hemostasis Flashcards Quizlet

Physiology Ch 14 Blood System Class Notes Part 2b Components Of Blood Platelets Fourth Component Flashcards Quizlet
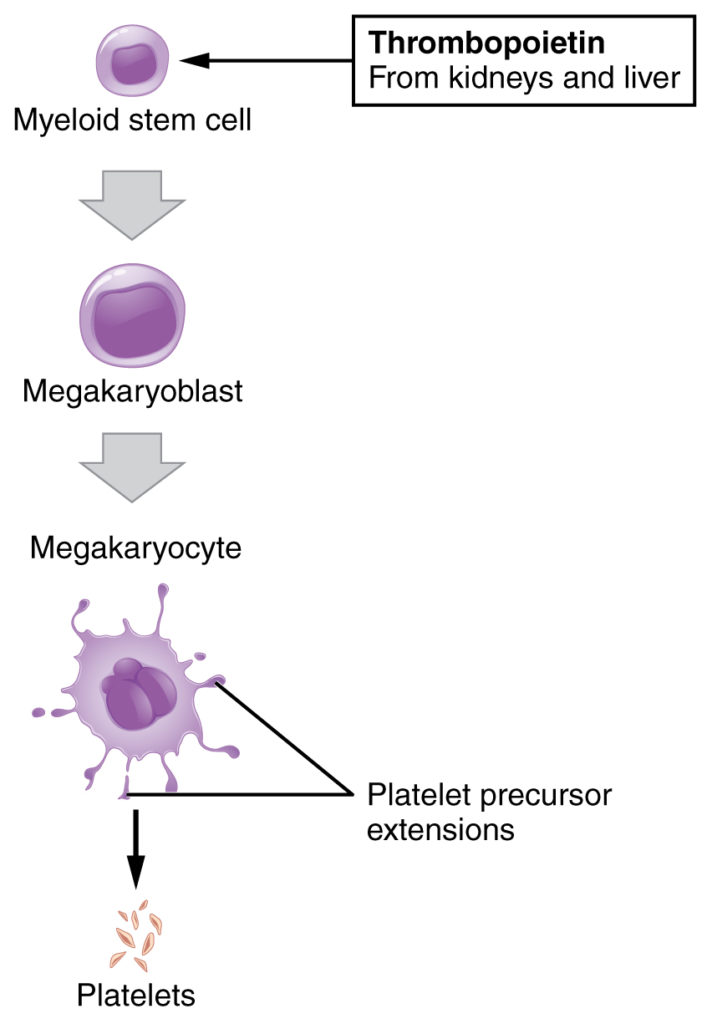
Leukocytes And Platelets Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Platelet Production Structure And Function Flashcards Quizlet

Platelets Hemostatic Plug Flashcards Quizlet

Platelet Function Flashcards Quizlet

Hemostasis Objectives Section 2 4 In Progress Flashcards Quizlet

Hemostasis Platelets And Approach To The Bleeding Patient Flashcards Quizlet

Heme Lecture 6 Platelets Flashcards Quizlet
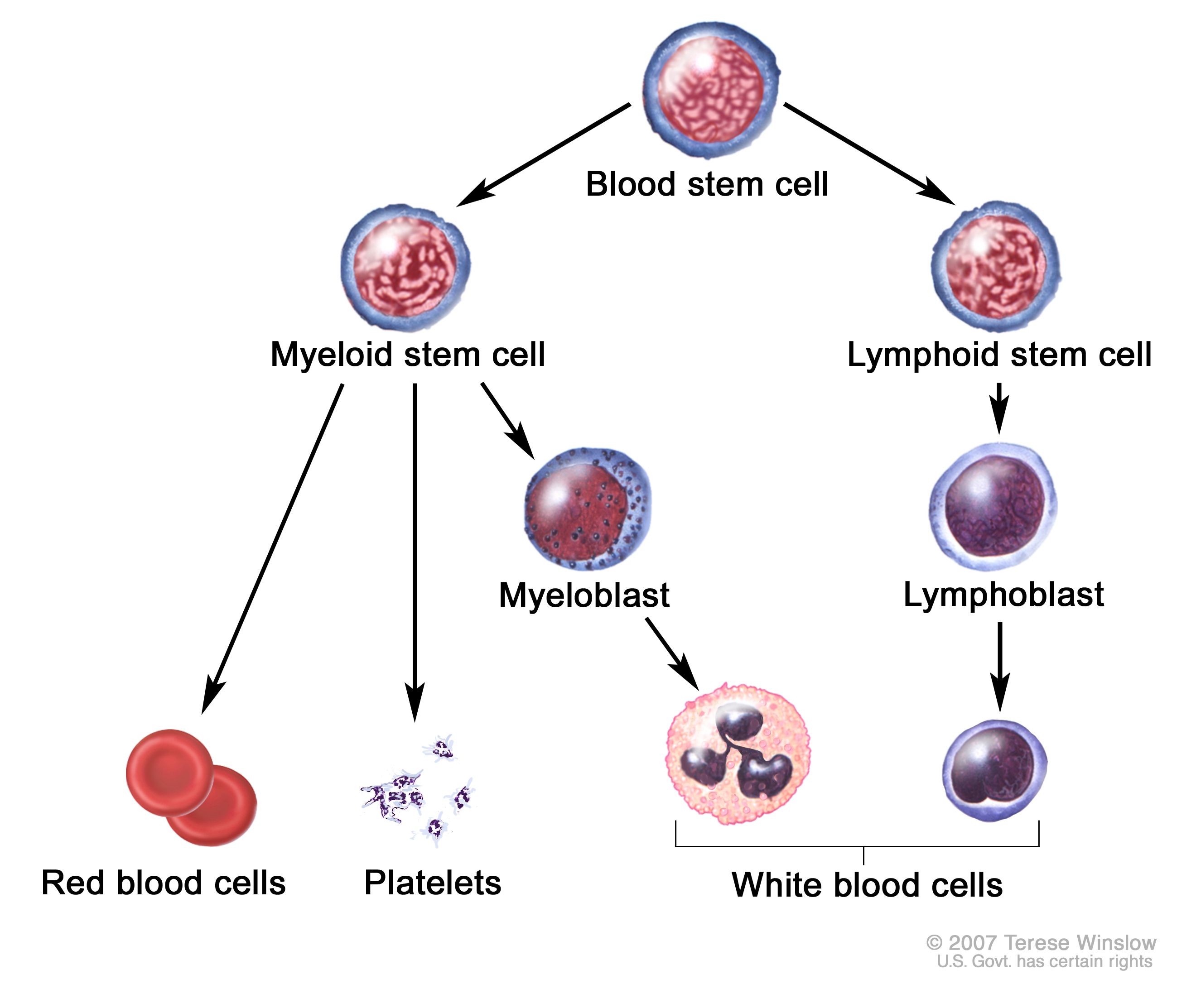
Definition Of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute

Platelets And Coagulation Ii Secondary Hemostasis Lecture 8 Exam 1 Flashcards Quizlet

Platelet Disorders Lecture 2 Flashcards Quizlet


Comments
Post a Comment